Thermal convection Simulator
Explore the principles of thermal convection and investigate how heat transfers in fluids. Adjust heating, container size, and fluid properties to visualize convection currents and temperature changes in real time with our interactive simulator.
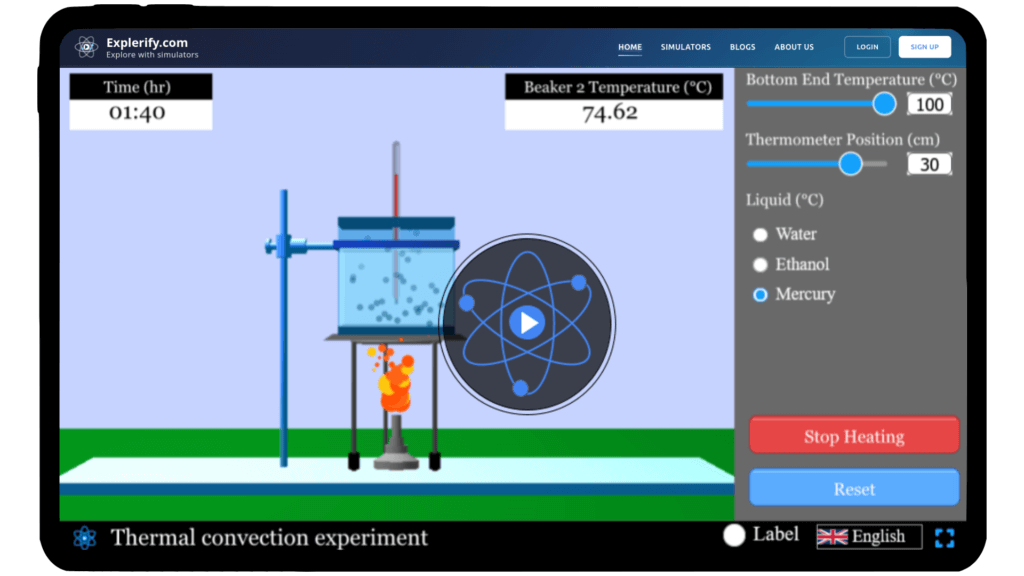
Thermal convection
Physics surrounds us, shaping how energy moves through the world around us, often in ways we don’t notice. Have you ever wondered how heat travels in fluids like water or air? This movement of energy, driven by density differences and fluid motion, is governed by the principles of thermal convection — and you can explore it with our interactive simulator. Adjust heating conditions, container dimensions, and fluid properties to observe convection currents forming and temperature changes over time. Start your journey into the fascinating world of thermal convection — experiment and visualize fluid heat transfer today!
\( \begin{align}
\dot{Q} = h A \left( T_s – T_\infty \right)
\end{align} \)
Mathematical description
where:
- \( \dot{Q} \) is the heat transfer rate (W)
- \( h \) is the convective heat transfer coefficient (W/m²·K)
- \( A \) is the surface area through which heat is transferred (m²)
- \( T_s \) is the surface temperature (°C or K)
- \( T_\infty \) is the temperature of the surrounding fluid far from the surface (°C or K)
- \( T(z,t) \) is the temperature of the fluid at height z and time t (°C or K
FAQs on thermal convection
Qus 1. What is thermal convection?
Thermal convection is the transfer of heat in fluids (liquids or gases) through the bulk movement of the fluid itself. Warmer fluid rises while cooler fluid sinks, creating convection currents that distribute heat.
Qus 2. How does thermal convection differ from conduction and radiation?
Conduction: Heat transfer through direct contact in solids.
Convection: Heat transfer in fluids via motion of the fluid.
Radiation: Heat transfer through electromagnetic waves without needing a medium.
Qus 3. What causes convection currents in fluids?
Convection currents are caused by differences in fluid density due to temperature variations. Warmer fluid becomes less dense and rises, while cooler, denser fluid sinks, forming circulating patterns.
Qus 4. What are some common examples of thermal convection?
Boiling water in a pot.
Ocean currents and atmospheric circulation.
Heating a room with radiators.
Convection in the Earth’s mantle causing plate tectonics.
Qus 5. Why is thermal convection important in everyday life and industry?
Convection plays a crucial role in heating and cooling systems, weather patterns, industrial processes like chemical reactors, and even cooking. It helps distribute heat efficiently.
Qus 6. How can I visualize convection in the simulator?
By adjusting the heating source, fluid properties, and container dimensions, you can observe convection currents forming in real time. The simulator shows how temperature changes at different heights in the fluid.
Qus 7. Can convection occur in solids?
No. Convection requires fluid movement. In solids, heat transfer occurs mainly through conduction.
Qus 8. What factors affect the speed and strength of convection currents?
Temperature difference between the hot and cold regions.
Fluid density and viscosity.
Shape and size of the container.
External forces like stirring or fans