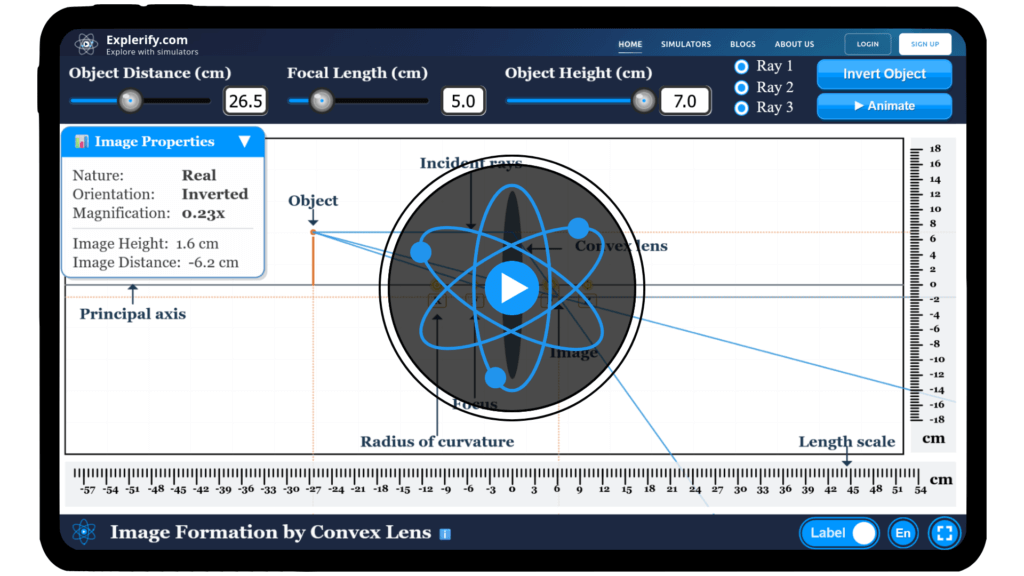
Convex lens simulator
Explore how convex lenses form images and experiment with different configurations to see their effects using our interactive simulator.
Convex lens
Have you ever wondered how magnifying glasses make objects appear larger or how cameras focus light to capture clear images?
The secret lies in the convex lens, a fascinating optical tool that bends light to create vivid and detailed images. Convex lenses, which are thicker in the middle than at the edges, converge light rays to a focal point, enabling them to form both real and virtual images. Our simulator vividly illustrates the working of this optical tool, allowing you to explore the intricacies of convex lens.
Dive into our simulator below, experiment with the controls and observe the resulting changes. Start simulating now!
$$ \frac{1}{f} = \frac{1}{v} – \frac{1}{u} $$
Mathematical description
Lens formula expresses the relationship between the focal length, object distance, and image distance for a lens.
where:
- \( f \) is the focal length of mirror
- \( u \) is the object distance
- \( v \) is the image distance
Tutorial video
Take a quick spin through our simulator!
FAQs on Convex Lens
Qus 1. What is a convex lens?
A convex lens is a lens that is thicker at the center than at the edges, causing parallel light rays to converge to a focal point. It is used to magnify objects and focus light, forming real or virtual images depending on the object’s distance from the lens. Convex lenses are commonly found in devices like magnifying glasses, cameras, and eyeglasses.
Qus 2. What are the properties of a convex lens?
Convex lenses can converge light rays, form real and virtual images, and magnify objects.
They form an image by bending light rays to meet at a focal point. The nature of the image (real or virtual, magnified or reduced) depends on the object’s distance from the lens.
Qus 3. What is the difference between a real image and a virtual image?
A real image is formed when light rays converge and can be projected onto a screen. A virtual image is formed when light rays appear to diverge from a point and cannot be projected onto a screen.
- In the case of a convex lens, when an object is positioned within the focal length, convex lens create a virtual, upright, and magnified image of the object.
- And, when an object is positioned beyond the focal length, convex lens creates a real, inverted and reduced image of the object.
Qus 4. What are the uses of convex lenses?
Convex lenses are used in magnifying glasses, cameras, microscopes, and telescopes to focus light and form images.
Convex lenses are also used in eyeglasses to correct hyperopia (farsightedness) by converging light rays before they enter the eye, helping to focus the image on the retina.
Qus 5. What is the focal length of a convex lens?
The focal length is the distance from the center of the lens to the focal point, where parallel rays of light converge.
Qus 6. What is the lens formula and how is it used?
The lens formula is
$$ \frac{1}{f} = \frac{1}{v} – \frac{1}{u} $$
where:
f is the focal length,
v is the image distance, and
u is the object distance. It is used to calculate the position and nature of the image formed by the lens.
Qus 7. How do you determine the focal length of a convex lens experimentally?
You can determine the focal length by focusing parallel rays of light (such as sunlight) onto a screen and measuring the distance from the lens to the point where the light converges
Qus 8. What are the ray-tracing rules for convex lens?
The following are the ray-tracing rules for convex lens:
- A ray that is initially traveling parallel to the central axis of the lens will pass through the focal point for a convex lens.
- A ray that will initially pass through the focal point of the lens will emerge parallel to the central axis of a convex lens.
- A ray that is directed through the center of will emerge with no change in direction.
Qus 9. Why convex lens is used in projectors?
Convex lens is used as projection lens in a projector. The projection lens is placed between the image slide and screen. The convex lens refract light rays from each pixel of the image slide and focuses them on the screen. This way the convex lens helps project a focused, clear and magnified image on the screen. If you want to learn about the projector’s workings, then do give a read to this article.


This is the correct blog for anybody who needs to seek out out about this topic. You notice so much its nearly onerous to argue with you (not that I actually would need…HaHa). You definitely put a new spin on a subject thats been written about for years. Great stuff, simply great!
Thank you, Manie! We’re happy to hear you enjoyed it and found it useful. We really appreciate you taking the time to share this.