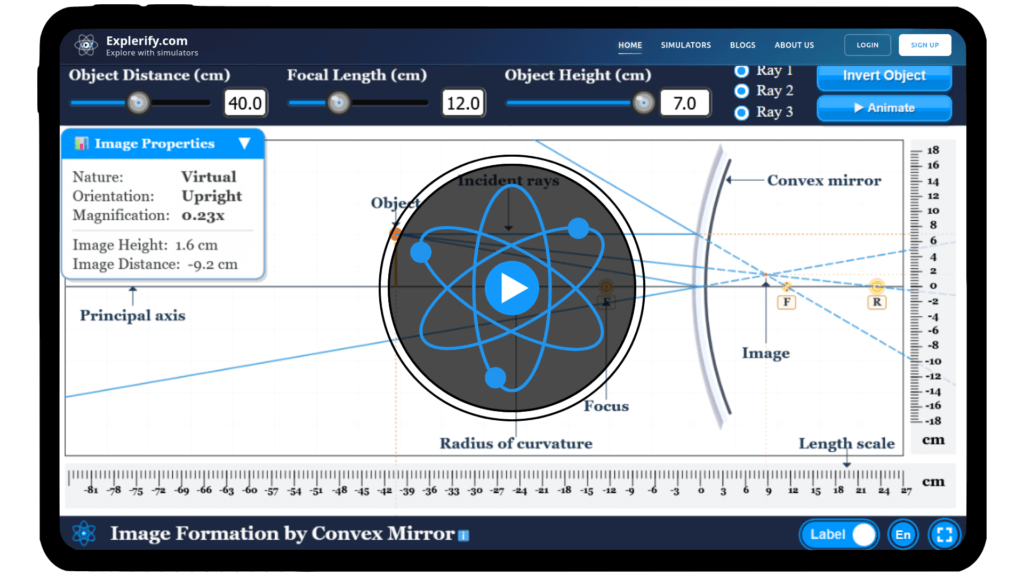
Convex mirror simulator
Explore how convex mirror form images and experiment with different configurations to see their effects using our interactive simulator.
Convex mirror
Convex mirrors, with their outward-curved reflective surfaces, are pivotal in applications from traffic mirrors to security installations. Curious about how convex mirrors expand your field of view or enhance safety on the road?
Step into the realm of convex mirrors with our immersive simulator, designed to unveil their optical marvels.Our simulator not only explains the science behind these mirrors but also allows you to manipulate focal lengths and object distances to witness real-time effects. Embark on an exploration of how convex mirror bends light to create panoramic perspectives and increase awareness. Start your journey below and revolutionize your understanding of optics!
$$ \frac{1}{f} = \frac{1}{v} + \frac{1}{u} $$
Mathematical description
Mirror formula relates the object distance, image distance, and focal length of a mirror.
where:
- \( f \) is the focal length of the mirror
- \( u \) is the object distance
- \( v \) is the image distance
Tutorial video
Take a quick spin through our simulator!
FAQs on convex mirror
Qus 1. What is a convex mirror?
A convex mirror is a spherical mirror with an outward-curved reflective surface. It diverges light rays, providing a wider field of view, and is commonly used for safety and security purposes.
Qus 2. How does a convex mirror form an image?
A convex mirror works by reflecting light rays outward, causing them to diverge. This creates a smaller, virtual image that appears to be located behind the mirror, making objects look smaller and further away.
Qus 3. What are the uses of a convex mirror?
Convex mirrors are used in vehicle side mirrors, security mirrors, and hallway safety mirrors. They provide a broad field of view, enhancing visibility and reducing blind spots.
Qus 4. Do convex mirror produce real images?
No, Convex mirrors only produce virtual, upright and diminished images. The image appears smaller and is located behind the mirror, making objects look further away than they actually are.
Qus .5 What is the principal focus and focal length of a convex mirror?
The principal focus of a convex mirror is the point where parallel light rays appear to diverge from after reflecting off the mirror. It is located behind the mirror and is virtual.
The focal length of a convex mirror is the distance from the mirror’s surface to its focal point, which is virtual and located behind the mirror. It is always positive and half the radius of curvature.
Qus 6. How does the curvature of a convex mirror affect its image?
Concave mirrors converge light to a focal point and can produce real or virtual images, whereas convex mirrors diverge light, forming only virtual images. Concave mirrors magnify, while convex mirrors provide a wider field of view.
Qus 7. How to calculate the image distance in a convex mirror?
In order to calculate the image distance in a convex mirror, we need to use the mirror formula.In the mirror formula below, ‘f’
$$ \frac{1}{f} = \frac{1}{v} + \frac{1}{u} $$
Qus 8. What is the difference between concave and convex mirrors?
Concave mirrors converge light to a focal point and can produce real or virtual images, whereas convex mirrors diverge light, forming only virtual images. Concave mirrors magnify, while convex mirrors provide a wider field of view.
Qus 9. What are the ray-tracing rules for spherical mirrors like convex mirror?
- A ray that is travelling parallel to the central axis of the convex mirror reflects back and appears to pass through the focal point of convex mirror (when traced back).
- A ray that appears to pass through the focal point of convex mirror, reflects back parallel to the central axis of the convex mirror.
- A ray that appears to pass through the centre of curvature of the convex mirror is reflected back upon itself.
- A ray that strikes the intersection of the mirror and central axis of the convex mirror is reflected symmetrically about the central axis