Fresnel Biprism Simulator
Investigate the phenomenon of Fresnel’s biprism and experiment with varying prism angles and light wavelengths to observe interference patterns using our interactive simulator.
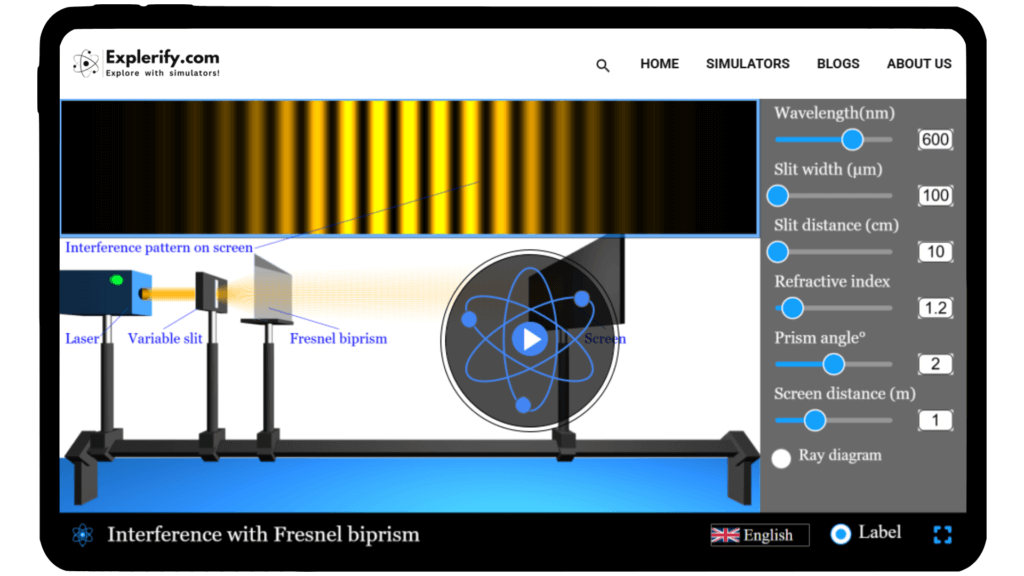
Fresnel Biprism
Physics shapes the way we perceive the world, often revealing hidden wonders through light and waves. Have you ever wondered how a single beam of light can split into two and create a striking interference pattern? This is the essence of Fresnel’s Biprism experiment — a clever setup that demonstrates the wave nature of light. With our interactive simulator, you can recreate this experiment virtually. Adjust prism angles, vary wavelengths, and watch interference fringes come alive. Step into the fascinating world of optics and explore the beauty of Fresnel’s Biprism today!
\(\beta = \frac{\lambda D}{2l (\mu – 1)\theta} \)
Mathematical description
where:
- \( \beta \) fringe width (distance between two consecutive bright or dark fringes)
- \( D \) biprism–screen distance
- \( \lambda \) is the wavelength of the light
- \( l \) slit–biprism distance
- \( \mu \) refractive index of biprism material
- \( \theta \) refracting angle of one half of the biprism
FAQs on Fresnel Biprism
Qus 1. What is a Fresnel Biprism?
A Fresnel biprism is an optical device made of two prisms joined at their bases, designed to split light from a single source into two virtual sources. The overlapping of these sources produces interference fringes, making it a key experiment to study the wave nature of light.
It was invented in the 19th century by Augustin-Jean Fresnel, who used it to give strong experimental proof of light’s wave behavior.
Qus 2. What is the principle of Fresnel Biprism experiment?
The Fresnel biprism experiment works on the principle of interference of light. A single slit light source is divided into two coherent virtual sources by the biprism, and their overlapping waves produce bright and dark fringes.
Qus 3. How does a Fresnel Biprism work?
The biprism refracts light from a narrow slit source, forming two virtual coherent sources on either side of the original slit. The superposition of the waves from these virtual sources on a screen produces an interference pattern.
Qus 4. What are the properties of the interference fringes in Fresnel’s Biprism experiment?
The fringes are equally spaced and parallel.
The fringe width depends on the wavelength of light, the refractive index of the biprism, the prism angle, and distances in the setup.
Bright and dark fringes alternate due to constructive and destructive interference.
Qus 5. What are the applications of Fresnel Biprism?
Measurement of the wavelength of light.
Study of interference and verification of the wave nature of light.
Determination of the refractive index of liquids using biprism and liquid cell methods.
Educational demonstrations of wave optics.
Qus 6. What are the advantages of Fresnel Biprism?
The Fresnel biprism provides a simple setup to study interference and wavelength measurement. Unlike double slits, it avoids alignment issues by creating two virtual coherent sources from a single slit.
Qus 7. Why is monochromatic light used in Fresnel Biprism experiment?
Monochromatic light is used to produce clear and stable interference fringes. If white light is used, overlapping wavelengths create colored or blurred fringes, making measurements difficult.