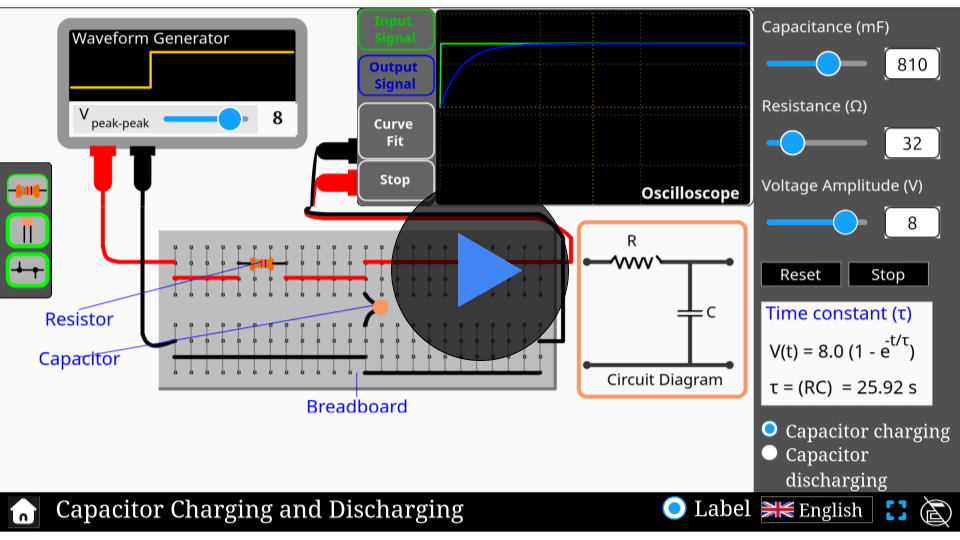
Galvanometer to ammeter simulator
Discover the transformation of a galvanometer into an ammeter with our interactive simulator: explore current measurement and the role of shunt resistors in expanding its range.
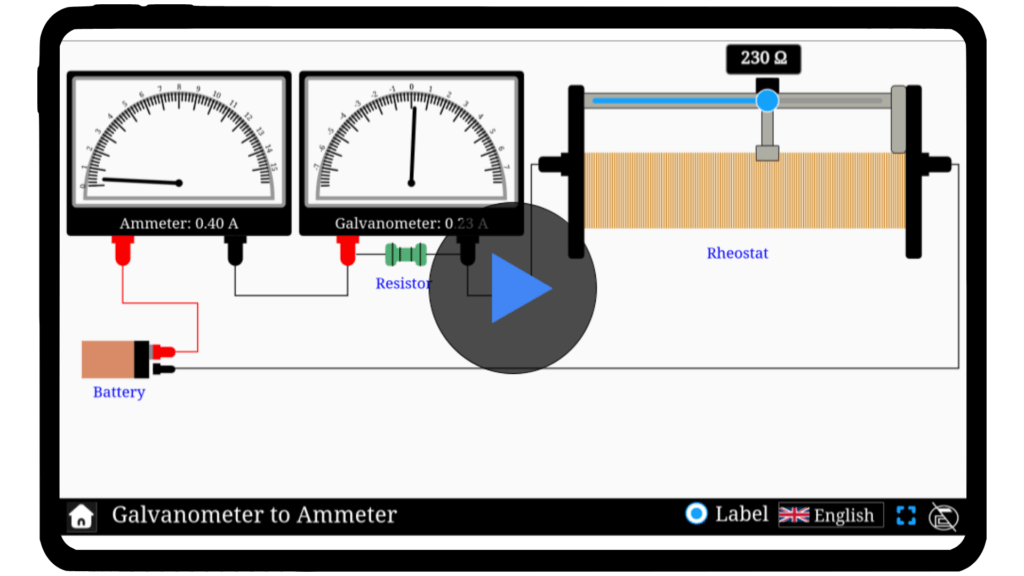
Galvanometer to ammeter
\( I_{max} = \frac{G}{S + G}
\)
Mathematical description
where:
- \( I_{max} \) is the maximum current ammeter can measure
- \( S \) is the shunt resistance
- \( G \) is the resistance of the galvanometer
Simulator
Explore the fascinating process of converting a galvanometer into an ammeter with our interactive simulator!
Interactive Physics Simulator – Galvanometer to Ammeter
🌟 You May Also Like
Suggested experiments and activities based on your progress...
FAQs on Galvanometer to Ammeter experiment
Qus 1. What is the aim of the galvanometer to ammeter experiment?
The aim is to convert a galvanometer (a sensitive current detector) into an ammeter (a current measuring device) by connecting a low resistance (shunt) in parallel.
Qus 2. How do you convert a galvanometer into an ammeter?
By connecting a low-value shunt resistor in parallel with the galvanometer so that most current bypasses the galvanometer.
Qus 3. What is the formula for the shunt resistance?
\[
S = \frac{I_g \times G}{I – I_g}
\]
Where S is shunt resistance, G is galvanometer resistance, Ig is full-scale deflection current, and I is the required ammeter range.
Qus 4. Why is the shunt placed in parallel with the galvanometer?
The shunt diverts excess current away from the galvanometer, protecting it and allowing the combination to measure larger currents.
Qus 5. What is the advantage of this conversion?
It lets a sensitive galvanometer handle higher currents, turning it into a practical ammeter for circuit use.
Qus 6. What is the typical range of a converted galvanometer-ammeter?
The range depends on the value of the shunt used, and it can be adjusted to suit various current ranges.