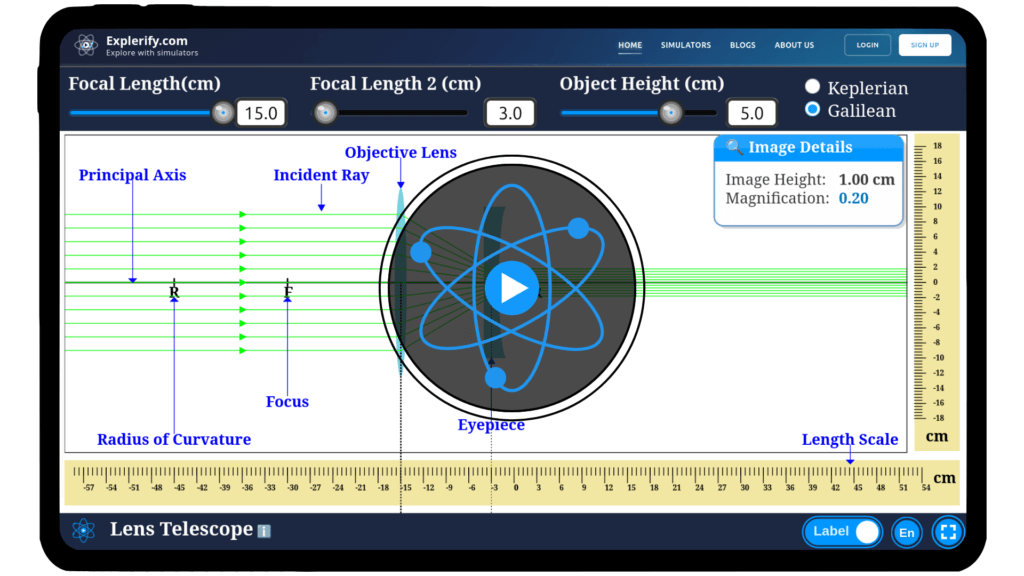
Lens telescope simulator
Explore the workings of Galilean and Keplerian telescopes with our virtual simulator, where you can interactively visualize and compare how each design focuses light and forms images of distant objects.
Lens telescope
Telescopes have long been the gateway to exploring the cosmos, bringing distant stars and galaxies into view through the power of lenses. The lens telescope, with its carefully aligned lenses, magnifies distant objects, enabling us to see details far beyond our natural eyesight. Curious to learn how this incredible instrument works?
With our interactive lens telescope simulator, you can experiment with focal lengths, lens distances, and object positioning to understand how light is manipulated to form magnified images. Embark on your journey into the world of optics and see for yourself how telescopes open windows to the universe!
\( m = \frac{f_{o}}{f_{e}}
\)
Mathematical description
Magnification of telescope is directly proportional to objective lens and inversely proportional to eyepiece lens.
where:
- \( f_{o} \) is the focal length of the objective lens
- \( f_{e} \) is the focal length of the eyepiece lens
Simulator
Dive into the physics of lens telescopes: Keplerian and Galilean designs. Adjust the focal lengths of the objective lens and eyepiece to explore how they influence the telescope’s magnification!
Interactive Physics Simulator – Image Formation by Concave Mirror
🌟 You May Also Like
Suggested experiments and activities based on your progress...
FAQs on Lens Telescope
Qus 1. What is the difference between a Keplerian and Galilean telescope?
A Keplerian telescope uses two convex lenses, providing an inverted image with a wide field of view, making it ideal for astronomical use. A Galilean telescope uses a convex objective lens and a concave eyepiece, providing an upright image with a narrower field of view, commonly used for terrestrial applications.
Qus 2. In a lens telescope what is the difference between objective and eyepiece lens ?
In a lens telescope, the objective lens collects light from distant objects and forms a real, inverted image, while the eyepiece magnifies this image for viewing. The objective has a long focal length for detailed image formation, whereas the eyepiece has a short focal length to enhance magnification. Together, they determine the telescope’s power using the formula: \( m = \frac{f_{o}}{f_{e}}
\)
Qus 3. How does a Keplerian telescope work?
A Keplerian telescope consists of a convex objective lens that collects and focuses light, creating an inverted image. The convex eyepiece lens magnifies this image. Its design offers high magnification, making it perfect for stargazing and observing celestial objects.
Qus 4. Why does the Galilean telescope produce an upright image?
The Galilean telescope uses a concave lens as its eyepiece, which intercepts the light rays before they converge. This optical setup ensures that the final image remains upright, making it suitable for viewing distant objects on Earth.
Qus 5. Which telescope is better for astronomy: Keplerian or Galilean?
The Keplerian telescope is better for astronomy due to its wider field of view and higher magnification, which allows for detailed observation of celestial objects. The Galilean telescope is more suited for terrestrial use due to its upright image and compact design.
Qus 6. What are the limitations of a Galilean telescope?
The Galilean telescope has a narrow field of view and lower magnification compared to the Keplerian telescope. Additionally, its concave eyepiece makes it difficult to correct for optical aberrations, limiting its use for advanced astronomical observations.
Qus 7. What are the historical applications of the Galilean telescope?
The Galilean telescope was famously used by Galileo Galilei to observe celestial bodies, including the moons of Jupiter and the phases of Venus. Its design paved the way for modern optical telescopes.
Qus 8. Can a Keplerian telescope be used for terrestrial purposes?
While a Keplerian telescope can technically be used for terrestrial purposes, its inverted image requires additional optics to correct orientation, making it less practical compared to a Galilean telescope.
Qus 9. What are the advantages of using a Keplerian telescope?
A Keplerian telescope offers higher magnification, a wider field of view, and better image clarity for celestial observations. It is also more compatible with advanced optical accessories like eyepieces for deep-space viewing.
Qus 10. How did lens telescopes revolutionize astronomy?
Lens telescopes like the Galilean and Keplerian revolutionized astronomy by allowing humans to observe celestial objects in detail. They provided crucial evidence supporting heliocentrism and expanded our understanding of the universe.


Hey there! This is my first comment here so I just
wanted to give a quick shout out and say I really enjoy reading through your posts.
Thank you for your feedback! We’re delighted to hear you’re enjoying our content. We look forward to supporting your learning journey.