Resistivity of a wire with a meter bridge simulator
Explore resistivity interactively: measure the resistivity of a wire using a meter bridge in our engaging simulator.
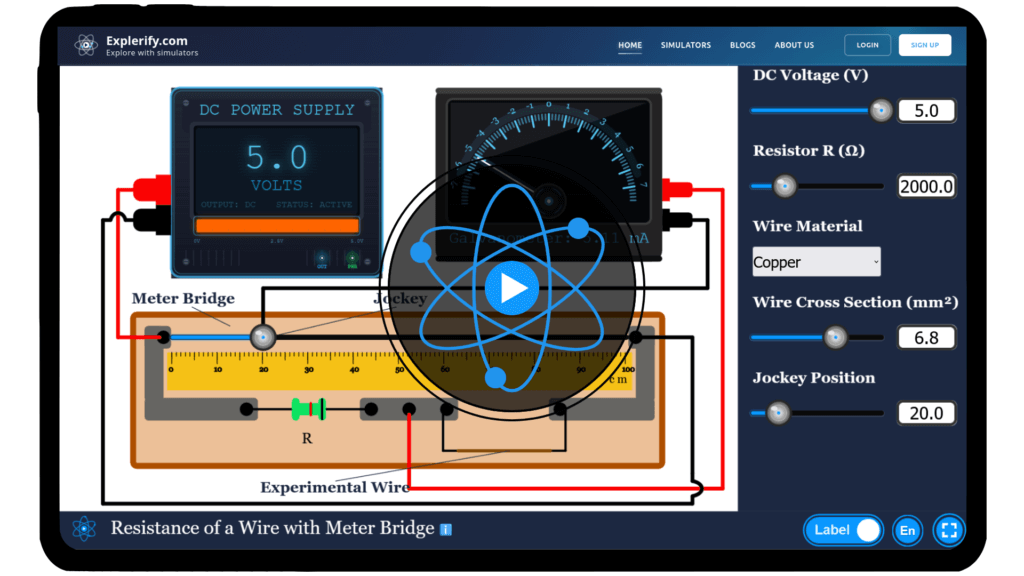
Resistivity of a wire with a meter bridge
Electricity flows through the wires that connect our world, but have you ever wondered how the resistivity of a wire is measured? Discover the science behind it with our interactive simulator. Use a meter bridge to calculate resistivity, adjust the parameters, and gain insights into this fundamental property of materials. Start exploring the physics of conductivity today!
\( \rho = \frac{V A}{I L}
\)
Mathematical description
where:
- \( V \) is the voltage across wire
- \( I \) is the current flowing through wire
- \( L \) is the length of the wire
- \( A \) is the area of the wire
- \( \rho \) is the resistivity of the wire
Simulator
Dive into the physics of electrical resistivity with our interactive Meter Bridge Simulator!
Interactive Physics Simulator – Resistivity with Meter Bridge
🌟 You May Also Like
Suggested experiments and activities based on your progress...
FAQs on Resistivity of a wire with a meter bridge
Qus 1. What is a meter bridge used for in physics?
A meter bridge is a device based on Wheatstone bridge principle used to compare and find unknown resistance values accurately.
Qus 2. How is resistivity of a wire calculated using a meter bridge?
We will find the resitivity of the resistor by using the formula \( \rho = \frac{V A}{I L}
\),
where V is the voltage, A is cross-sectional area and L is the length of the resistor
Qus 3. What principle does the meter bridge work on?
It works on the Wheatstone bridge principle, which states that the bridge is balanced when the ratio of two known resistors equals the ratio of the other two.
Qus 4. Why is a jockey used in a meter bridge experiment?
The jockey is used to make sliding contact along the wire to find the null point where no current flows through the galvanometer.
Qus 5. How is the balance point found in a meter bridge?
The balance point is found when the galvanometer shows zero deflection, indicating the bridge is balanced and the ratio of resistances is equal.
I admire your work, appreciate it for all the informative content.
whoah this blog is wonderful i love reading your posts. Keep up the good work! You know, a lot of people are hunting around for this info, you can aid them greatly.
I was ɑble to find good info from your blog pοsts.
Dear Cole,
We are really glad you found the posts helpful. 😊