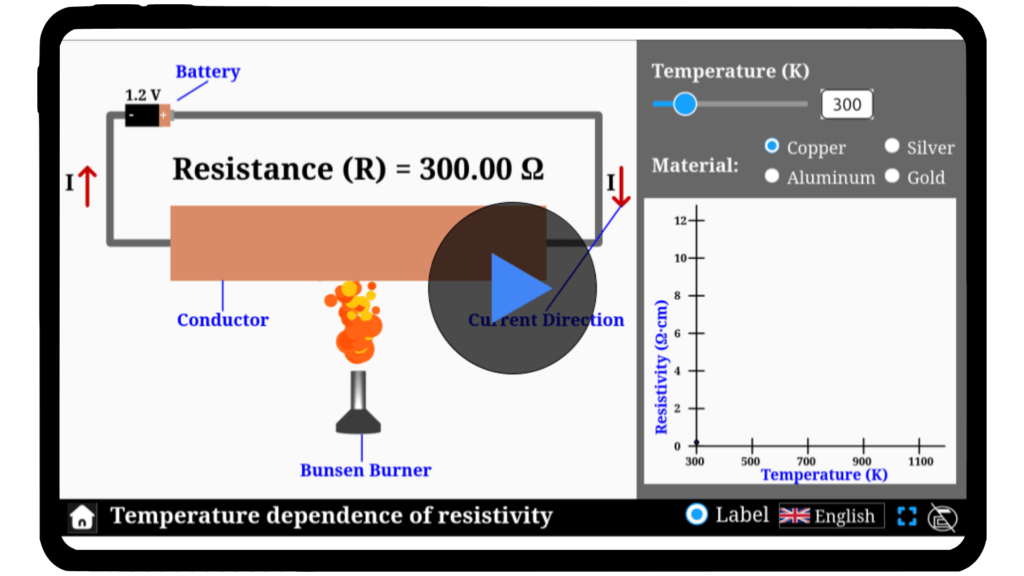
Temperature dependence of resistivity simulator
Discover how temperature shapes the resistivity of materials! Use our simulator to explore the thermal effects on electrical conduction in different materials.
Temperature dependence of resistivity
Did you know that temperature can significantly affect a material’s ability to conduct electricity? Metals like copper and aluminum become less conductive as temperature increases, while some materials behave differently. Our temperature-dependent resistivity simulator lets you investigate these fascinating relationships. Adjust the temperature, select different materials, and visualize how resistivity evolves. Start experimenting and uncover the science behind thermal effects on electrical conductivity!
\( \rho(T) = \rho_0 \left[ 1 + \alpha (T – T_0) \right]
\)
Mathematical description
where:
- \( \rho(T) \) is the resistivity at temperature \( T \).
- \( \rho_0 \) is the resistivity at a reference temperature \( T_0 \) (usually \( 20^\circ\text{C} \)).
- \( \alpha \) is the temperature coefficient of resistivity, a material-specific constant (in \( K^{-1} \)).
- \( T \) is the temperature at which resistivity is being measured (in \( K \) or \( ^\circ\text{C} \)).
- \( T_0 \) is the reference temperature (in \( K \) or \( ^\circ\text{C} \)).
Simulator
Explore the fascinating physics of temperature-dependent resistivity with our interactive Temperature Dependence Simulator!
Interactive Physics Simulator – Temperature Dependent Resistivity
🌟 You May Also Like
Suggested experiments and activities based on your progress...
FAQs on Temperature dependence of resistivity
Qus 1. What is temperature dependent resistivity?
Temperature dependent resistivity refers to how a material’s electrical resistivity changes with temperature. Most conductors show increased resistivity as temperature rises.
Qus 2. How does temperature affect resistivity in metals?
In metals, resistivity increases with temperature because atoms vibrate more, scattering electrons and impeding their flow.
Qus 3. What is the formula for temperature dependent resistivity?
The formula is:
\( \rho(T) = \rho_0 \left[ 1 + \alpha (T – T_0) \right]
\)
where \( \rho_0 \) is original resistivity, \( \alpha \) is the temperature coefficient, and T is the temperature.
Qus 4. Why does resistivity decrease with temperature in semiconductors?
In semiconductors, resistivity decreases with temperature because more free charge carriers (electrons and holes) are generated at higher temperatures.
Qus 5. What is the temperature coefficient of resistivity?
It’s a constant \( \alpha \) that quantifies how much a material’s resistivity changes per degree of temperature change.
Qus 6. Do insulators show temperature dependent resistivity?
Yes, insulators also show changes in resistivity with temperature, but the effect is complex and depends on the material’s structure.
copper, aluminum
I like this site its a master peace ! .