Stop Internet Spies: Protect Your Privacy with a Faraday Bag
I was just talking about how my laptop was getting slow, and guess what? Almost instantly, I got an Amazon ad for a new laptop on my phone. While it was arguably useful, I couldn’t help but feel irritated. To me, it was a clear example of internet companies eavesdropping and breaching my privacy. However, my friend sitting across the table had a completely different perspective. He thought I was overreacting—calling it a harmless ad that showed up at just the right time when I actually needed a laptop. According to him, I should be grateful for the convenience.
I’m sure many of you have had similar debates within your friend groups. Some might see this as a significant invasion of privacy, while others may dismiss it as a trivial or even helpful part of modern technology. But no matter which side of the argument you fall on, one thing is certain: we are all increasingly aware that internet companies are listening in on us.
You might think you don’t have anything significant to hide, so internet companies prying on your data doesn’t seem like a big deal. But that’s where you’re mistaken. Unknowingly, you’re providing countless data points about yourself to third parties. These entities are not only storing this data but also profiling you, tracking your preferences, habits, and even vulnerabilities. In the event of a data breach, all this sensitive information could be exposed to the public or fall into the wrong hands.
This growing concern is why leading organizations worldwide are turning to Faraday bags to secure their smartphones and tablets—and I believe you should consider doing the same too.
Faraday bags create a protective shield that blocks electromagnetic signals from entering or leaving the enclosed space. Using the principles of a Faraday cage, they leverage conductive materials to neutralize external electromagnetic fields, ensuring your devices—and your data—stay secure.

Behaviour of Faraday bags upon interaction with electromagnetic waves
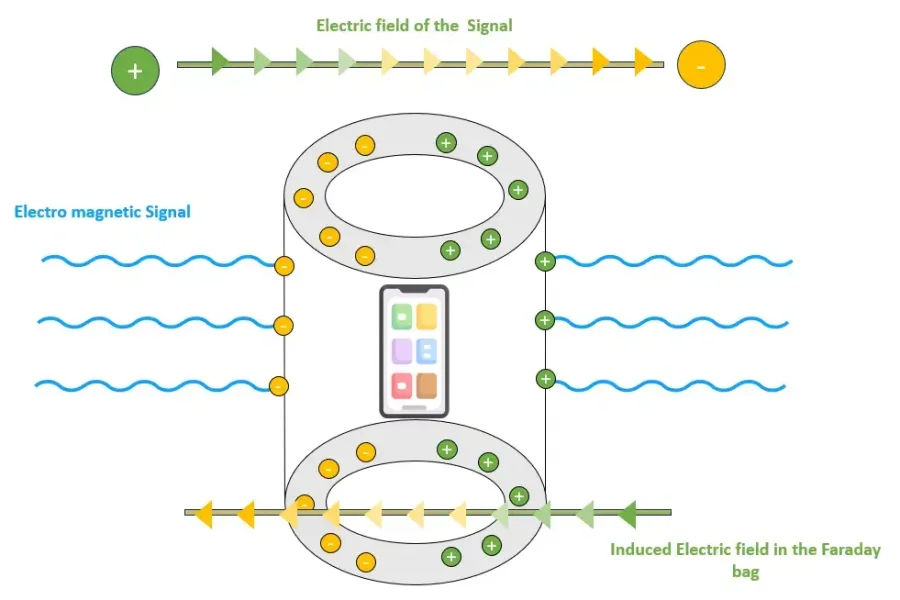
Faraday bags interact with electromagnetic (EM) waves in the following ways:
1. Reflection of EM Waves
The conductive materials in the Faraday bag, such as aluminum or copper, reflect the majority of the incoming electromagnetic waves. This prevents the waves from penetrating the bag and reaching any device inside it.
2. Absorption and Dissipation
A portion of the EM waves is absorbed by the conductive layers, where the energy is dissipated as heat. This further weakens the strength of the waves, ensuring minimal interference.
3. Redistribution of Electric Fields
The conductive surface redistributes the electric fields of the EM waves across the outer surface of the bag. This creates a uniform charge distribution that cancels the waves inside the enclosed space, effectively creating a signal-free environment. In Figure 2, we have schematically depicted how charge distribution happens within the Faraday bag.
4. Blocking Signal Transmission
Since the bag prevents EM waves from entering or leaving, devices inside the Faraday bag cannot transmit or receive signals, including Wi-Fi, cellular, Bluetooth, or GPS signals.
Material Composition
Faraday bags are made from layers of conductive materials, such as aluminum or copper, often sandwiched between flexible fabric or plastic. These materials reflect and absorb electromagnetic waves.
Applications of Faraday Bag
Faraday bags are widely used to:
- Protect devices from hacking, tracking, or signal interference.
- Prevent unauthorized access to RFID-based items like credit cards or passports.
- Shield electronics during sensitive investigations or when confiscating digital evidence.
To learn more about Faraday bag or Faraday cage in general, do check out the interactive Faraday cage simulator.




Good website! I truly love how it is simple on my eyes and the data are well written. I am wondering how I might be notified when a new post has been made. I have subscribed to your RSS feed which must do the trick! Have a nice day!