Transformer Simulator
Explore the working of transformers by adjusting coil turns, input voltage, and core materials to observe step-up, step-down, and efficiency behavior with our interactive simulator.
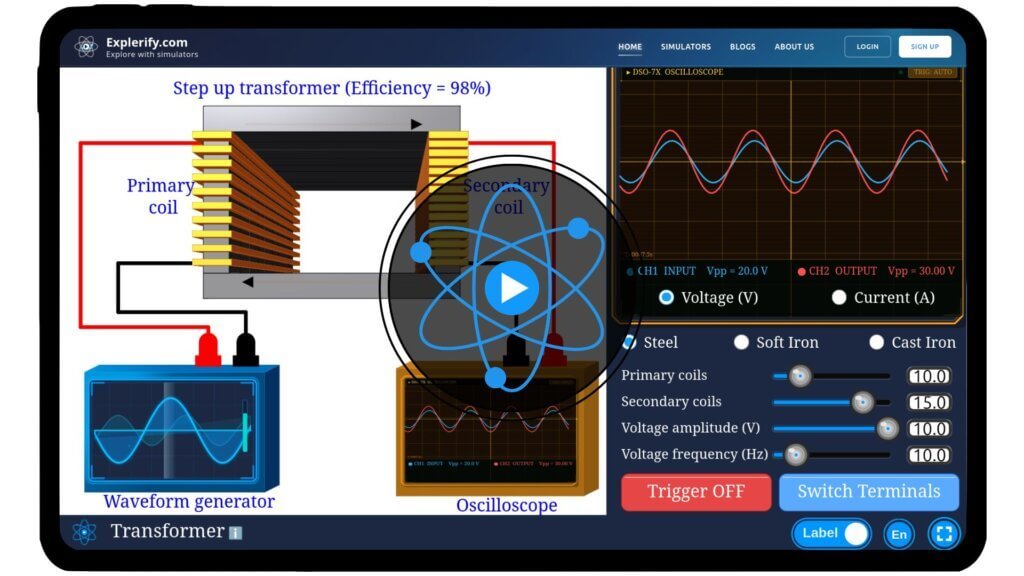
Transformer
Physics powers much of our modern world, often in ways we take for granted. Have you ever wondered how electricity is efficiently transmitted and transformed for everyday use? Transformers, the silent workhorses of electrical systems, step up or step down voltage using fascinating electromagnetic principles. With our interactive Transformer Simulator, you can explore this phenomenon hands-on. Adjust coil turns, input voltage, and core material, observe the resulting changes in output voltage, current, and efficiency, and uncover the science behind these essential devices. Start your journey into the world of electromagnetism — experiment with transformers today!
\( \frac{V_s}{V_p} = \frac{N_s}{N_p} \)
Mathematical description
where:
- \( V_s \) is the secondary voltage
- \( V_p \) is the primary voltage
- \( N_s \) is the number of turns in the secondary coil
- \( N_p \) is the number of turns in the primary coil
FAQs on Transformer
Qus 1. What is a transformer?
A transformer is an electrical device that transfers energy between two or more coils through electromagnetic induction, allowing voltage to be increased (step-up) or decreased (step-down).
Qus 2. How does a transformer work?
It works on the principle of electromagnetic induction: an alternating current in the primary coil creates a changing magnetic field, which induces a voltage in the secondary coil.
Qus 3.What is the role of the core material?
The core guides the magnetic flux between coils. Materials like soft iron or laminated steel reduce energy loss and improve efficiency.
Qus 4. How does a transformer’s efficiency depend on load and material?
Efficiency is affected by copper losses (I²R) in the windings and core losses (hysteresis and eddy currents). High-quality materials and proper design increase efficiency.
Qus 5. What is the difference between step-up and step-down transformers?
Step-up: increases voltage, decreases current.
Step-down: decreases voltage, increases current.
- A step-up unit has more turns on the secondary coil, thus raising voltage; a step-down has fewer turns on secondary coil, thus lowering voltage.
Qus 6. Can transformers work with direct current (DC)?
No, transformers only work with alternating current (AC) because a changing magnetic field is required to induce voltage in the secondary coil.
Qus 7. Do transformers change frequency?
A transformer does not change frequency; frequency in equals frequency out. If you feed 50 Hz, the secondary is also 50 Hz. Also we need to ensure that we match transformer frequency while feeding AC current. Using a 60 Hz-only transformer on 50 Hz can cause core saturation.
Qus 8. Where are transformers used in daily life?
Transformers are used in power transmission, electronic devices, chargers, voltage regulators, and many household appliances.
Qus 9. What are the main transformer losses?
Transformers have core (iron) losses and copper (winding) losses.
Core losses—hysteresis and eddy currents—occur whenever the unit is energized.
Copper losses are resistive (I²R) losses losses and increase with load current. Good design minimizes both types to improve efficiency.
Qus 10. How can transformers help in reducing power losses?
By stepping up voltage for long-distance transmission, transformers reduce current and therefore minimize resistive (I²R) losses in power lines.
Qus 11. How efficient are transformers?
Large power and distribution transformers commonly achieve efficiencies of 97–99% or higher. Efficiency depends on size, design, materials, and loading. Operating near the transformer’s optimal load point reduces losses. Proper maintenance also helps retain high efficiency over time.