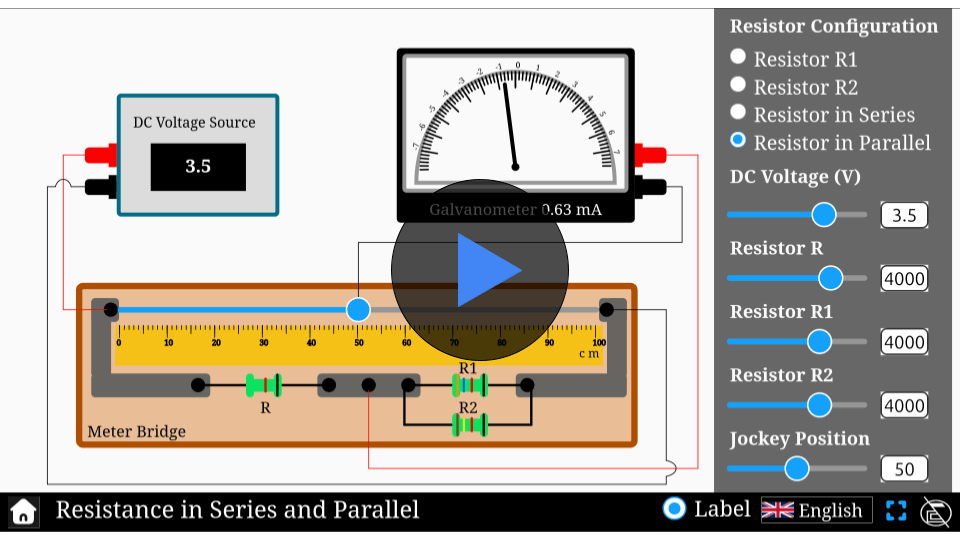
Resistivity of a conductor simulator
Unlock the secrets of electrical resistivity! With our interactive simulator, you can explore how the material, length, and cross-sectional area of a conductor affect its resistance.
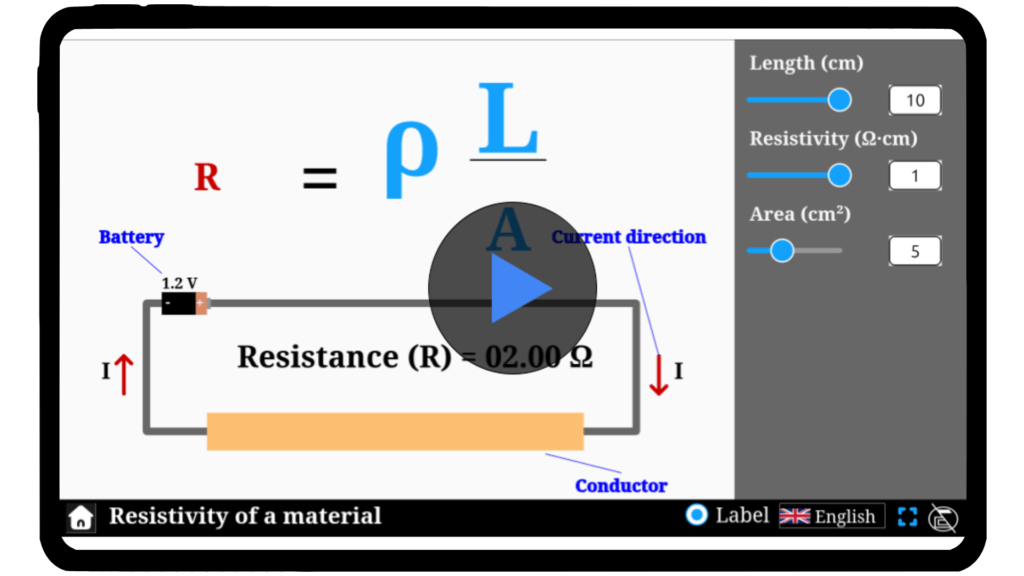
Resistivity of a conductor
Conductors play a pivotal role in the world of electricity. Have you ever wondered why some materials conduct electricity better than others, or why longer wires have higher resistance? Dive into our resistivity simulator to explore these questions firsthand. Experiment with different conductor materials, change their dimensions, and see how resistivity and resistance are interrelated. Start learning and experimenting now!
\( R = \rho \frac{L}{A}
\)
Mathematical description
where:
- \( L \) is the length of the conductor
- \( A \) is the area of cross section of conductor
- \( R \) is the resistance of the conductor
- \( \rho \) is the resistivity of conductor (material specific)
FAQs on Resistivity of a conductor
Qus 1. What is resistivity of a conductor?
Resistivity is a material’s intrinsic property that quantifies how strongly it resists the flow of electric current. It is denoted by ρ (rho) and measured in ohm-meters (Ω·m).
Qus 2. How is resistivity different from resistance?
Resistivity is a fixed property of a material, while resistance depends on the material’s dimensions and is calculated using R = ρL/A, where L is length and A is cross-sectional area.
Qus 3. What factors affect the resistivity of a conductor?
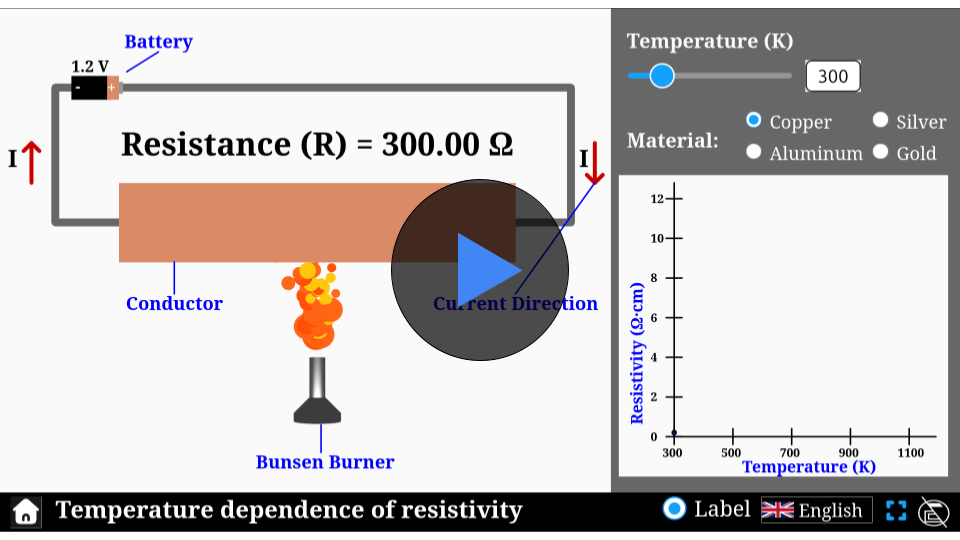
Resistivity depends mainly on the material type and its temperature — it usually increases with temperature in conductors.
Qus 4. How does temperature affect resistivity?
As temperature increases, resistivity typically increases in conductors due to more frequent collisions between electrons and atoms.
Qus 5. What is the SI unit of resistivity?
The SI unit of resistivity is ohm-meter (Ω·m).
Qus 6. Why is resistivity important in electrical design?
Resistivity helps engineers select the right materials for wiring and components to ensure efficiency and safety in electrical systems.
Qus 7. How does resistivity vary in different materials?
Conductors like copper have low resistivity, insulators like rubber have high resistivity, and semiconductors have intermediate values.
Qus 8. Which material has the lowest resistivity?
Silver has the lowest resistivity among all metals, making it the best natural conductor of electricity.