Galvanometer to voltmeter simulator
Transform a galvanometer into a voltmeter: explore voltage measurement principles interactively with our engaging simulator.
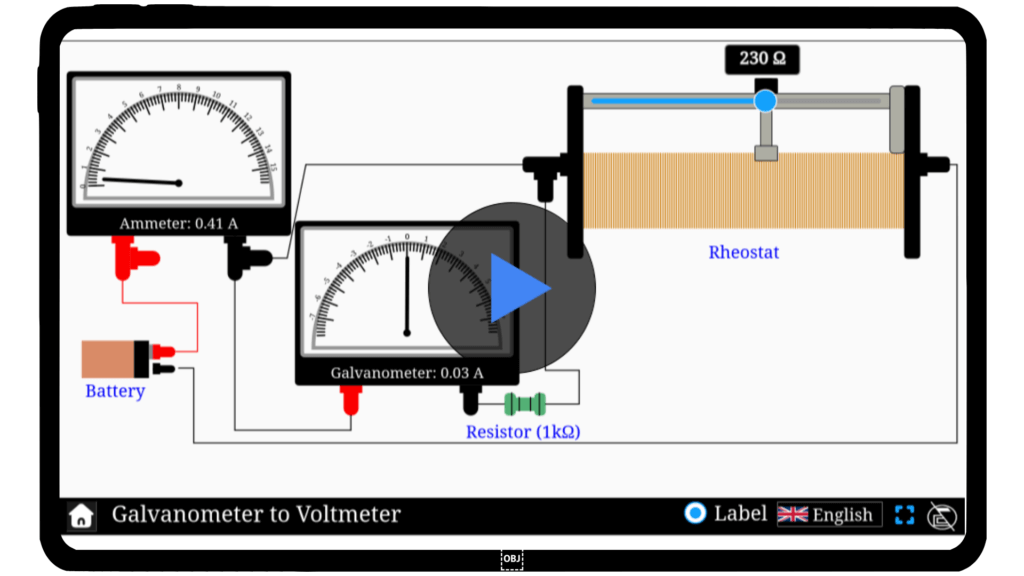
Galvanometer to voltmeter
Voltage measurement plays a key role in understanding electrical systems, from circuits in gadgets to industrial machinery. Ever wondered how a galvanometer can measure voltage? Dive into our interactive simulator to explore the transformation of a galvanometer into a voltmeter. Experiment with parameters, understand the mechanics, and uncover the science behind accurate voltage measurement. Start your journey into electrical exploration today!
\( V = I_{g} (R_{s} + R{g})
\)
Mathematical description
where:
- \( V \) is the voltage to be measured
- \( R_{s} \) is the Series resistance to be added
- \( I_{g} \) is the full-scale deflection current of the galvanometer
- \( R_{g} \) is the internal resistance of the galvanometer
FAQs on Galvanometer to Voltmeter experiment
Qus 1. What is the aim of the galvanometer to voltmeter experiment?
The aim is to convert a galvanometer into a voltmeter by connecting a high resistance in series, enabling it to measure potential difference.
Qus 2. How do you convert a galvanometer into an voltmeter?
By connecting a high-value resistance (R) in series with the galvanometer so it can measure voltage without drawing excess current.
Qus 3. What is the formula for the shunt resistance?
\[
R = \frac{V}{I_g} – G
\]
Where R is the required series resistance, V is the full-scale voltage, Ig is the galvanometer current, and G is its resistance.
Qus 4. Why is resistance connected in series with a galvanometer for voltmeter conversion?
The series resistance limits the current, allowing the galvanometer to measure voltage across components safely.
Qus 5. What is the range of the converted voltmeter?
The range depends on the series resistance chosen — higher resistance gives a higher voltage range.
Qus 6. Why can't a galvanometer measure voltage directly?
Because it’s too sensitive and would get damaged by typical voltages unless a series resistor limits the current.