Capacitor charging & discharging simulator
Discover the behavior of capacitors in action: explore the charging and discharging process interactively with our simulator.
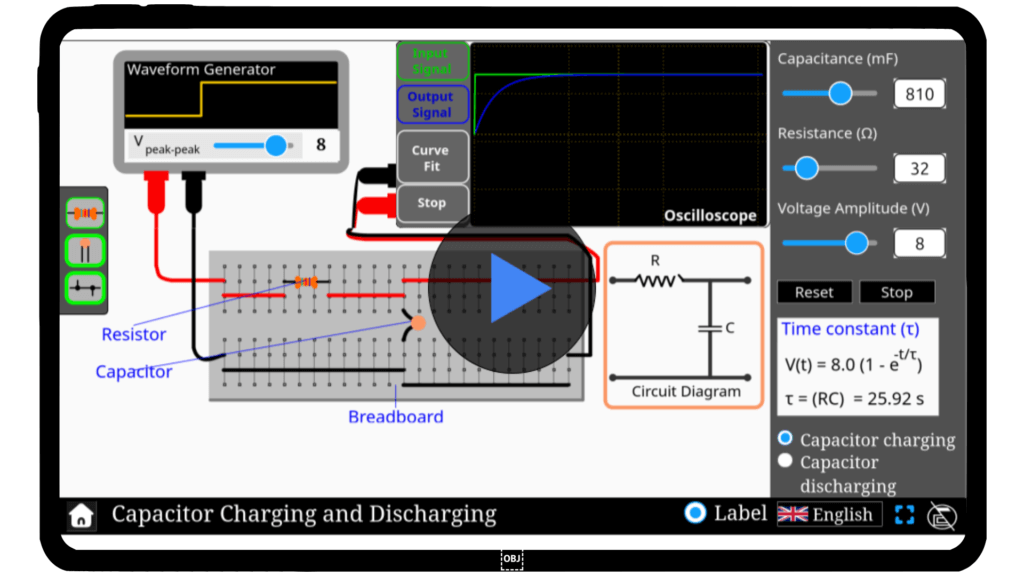
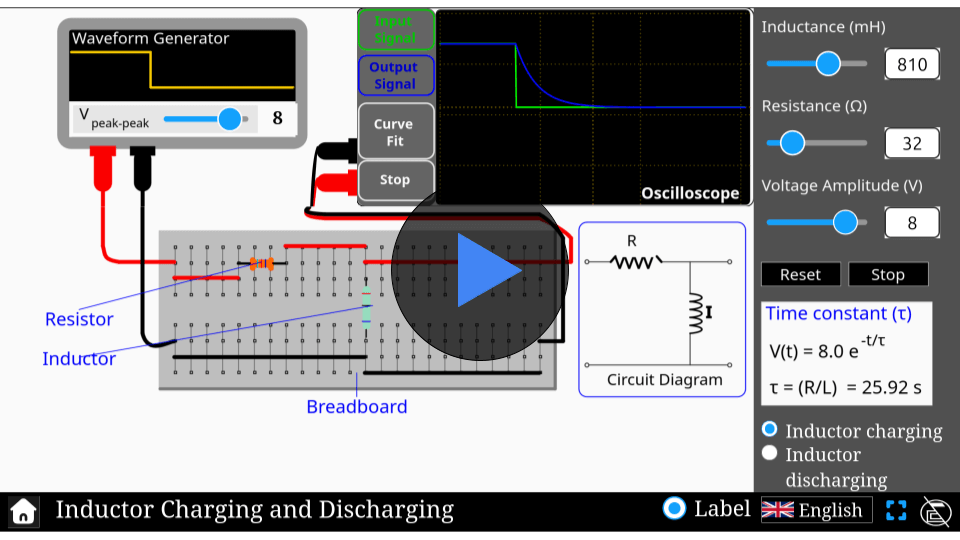
Capacitor charging & discharging
Capacitors play a crucial role in electrical circuits, storing and releasing energy. Ever wondered how they charge and discharge? Step into the world of capacitor behavior with our interactive simulator. Experiment with different parameters, observe the charging and discharging cycles, and understand the physics behind energy storage in capacitors. Start exploring today!
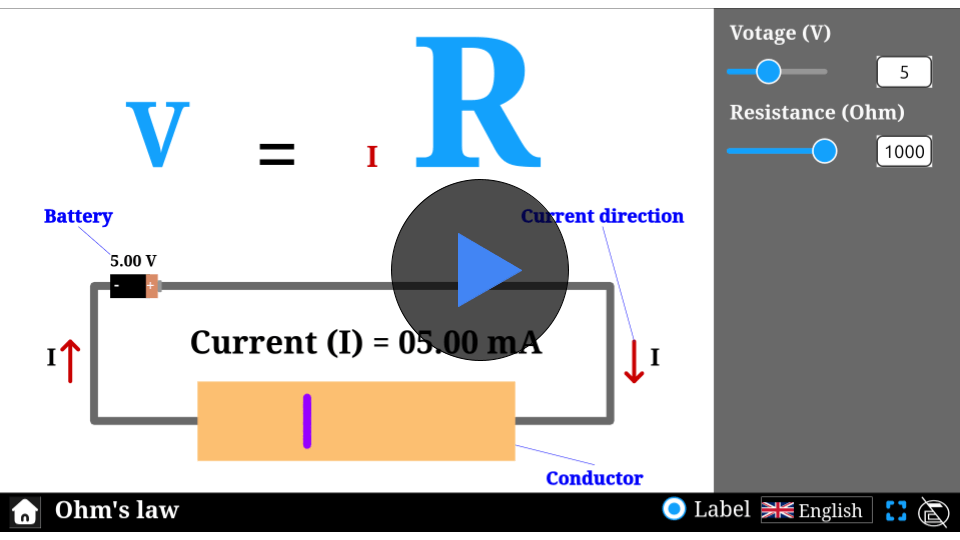
\( V = I R
\)
Mathematical description
where:
- \( V \) is the voltage across conductor
- \( I \) is the current flowing through conductor
- \( R \) is the resistance of the conductor
FAQs on Capacitor charging & discharging
Qus 1. What happens when a capacitor is charging?
When a capacitor charges, electrons accumulate on one plate, creating a voltage difference, and the current decreases exponentially over time.
Qus 2. What is the formula for capacitor charging?
The voltage across the capacitor during charging is: \[
V(t) = V_0 \left(1 – e^{-t/RC}\right)
\] where \( V_0 \) is supply voltage, R is resistance, \( C \) is capacitance, and \( t \) is time.
Qus 3. What happens when a capacitor discharges?
During discharge, the stored energy is released, current flows in reverse, and both voltage and current decay exponentially to zero.
Qus 4. What is the discharge formula of a capacitor?
The voltage during discharge is:\[
V(t) = V_0 e^{-t/RC}
\] This shows voltage decreases over time based on the \( RC \) time constant.
Qus 5. What is the time constant (\( RC \))?
\( RC \) is the time it takes for the voltage to drop to about 37% of its initial value. It controls how fast the capacitor charges or discharges.
Qus 6. Where is capacitor charging/discharging used in real life?
Capacitor charging and discharging are crucial in various real-life applications. Here are a few key uses:
1. Camera Flash
In a camera flash, capacitors charge up to store energy and then discharge quickly to produce a high-intensity light burst.
2. Timing Circuits
Capacitors are used in oscillators and timing circuits (like in clocks, radios, and pulse generators) to create delays or control the timing of signals.
3. Power Supply Filtering
In power supplies, capacitors charge and discharge to smooth out voltage fluctuations, providing steady DC output from an AC source.
4. Defibrillators
Capacitors in defibrillators store energy and then discharge it rapidly to deliver a shock to the heart in case of a medical emergency.
5. Signal Processing
In audio and RF circuits, capacitors charge and discharge to filter or modify signals, helping in things like volume control, noise reduction, and signal amplification.
6. Electric Vehicles
In electric vehicles and hybrid systems, capacitors (often in the form of supercapacitors) help smooth the flow of power between batteries and motors during acceleration or braking.
These applications leverage the charging and discharging properties of capacitors to control energy flow efficiently in various systems.