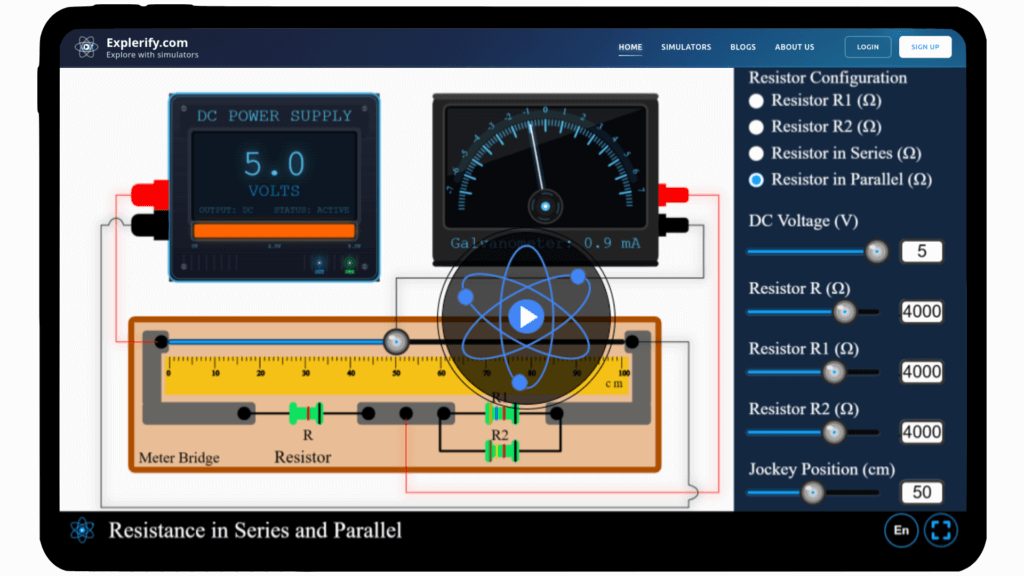
Resistor in series & parallel simulator
Experiment with resistors in series and parallel, and see how their configuration affects the overall resistance.
Resistor in series & parallel
Electricity flows through circuits in fascinating ways, but have you ever wondered how the arrangement of resistors affects the total resistance? Dive into the world of series and parallel circuits with our interactive simulator. Adjust resistor values, explore different configurations, and observe how resistance changes in real-time. Understand the core principles that shape electrical circuits — start your exploration today!
\( R_{series} = R_{1} + R_{2}
\)
\( \frac{1}{R_{parallel}} = \frac{1}{R_{1}} + \frac{1}{R_{2}}
\)
Mathematical description
where:
- \( R_{series} (R_{parallel}) \) is the effective resistance of the series(parallel) combination
- \( R_{1} (R_{2} \) is the resistance of resistor 1 (resistor 2)
Simulator
Explore resistance in series and parallel with our interactive simulator!
Interactive Physics Simulator – Resistor in Series and Parallel
Interactive Physics Simulator – Image Formation by Concave Mirror
🌟 You May Also Like
Suggested experiments and activities based on your progress...
FAQs on Resistance in Series and Parallel
Qus 1. What is resistance in series?
In a series circuit, resistances add up: \[ R_{series} = R_{1} + R_{2}
\]
The same current flows through each resistor.
Qus 2. What is resistance in parallel?
In a parallel circuit, the reciprocal of total resistance equals the sum of reciprocals: \[
\frac{1}{R_{parallel}} = \frac{1}{R_{1}} + \frac{1}{R_{2}}
\]
Voltage remains the same across each branch.
Qus 3. How does current behave in series and parallel circuits?
In series, current is the same through all resistors. In parallel, total current splits among branches based on resistance.
Qus 4. Which configuration has higher total resistance: series or parallel?
Series always has higher total resistance than parallel, assuming the same resistors.
Qus 5. What’s the practical use of series and parallel combinations?
Series is used for devices needing the same current (e.g. old-style Christmas lights), while parallel is ideal for home wiring to keep voltage constant across devices.
Qus 6. What happens to effective resistance when more resistors are added in series or parallel?
Adding resistors in series increases total resistance, making it harder for current to flow.
Adding resistors in parallel decreases total resistance, making it easier for more current to flow.
I wish to express my gratitude for your generosity for visitors who actually need assistance with this idea. Your real dedication to passing the solution all over ended up being extraordinarily good and have in every case helped women much like me to achieve their dreams. Your informative guidelines implies a great deal to me and substantially more to my mates. Thank you; from each one of us.