Speed of light
The speed of light has captivated human curiosity for centuries, standing as one of the greatest mysteries in science. Over time, brilliant minds have devised ingenious experiments to determine its exact value, evolving from rudimentary observations to sophisticated setups like the Michelson-Morley interferometer.
With our interactive simulator, you can explore this fascinating phenomenon firsthand. Adjust the variables, experiment with different conditions in this simplistic experiment setup , and watch how speed of light gets affected. Discover the science behind nature’s wonders — dive in and start experimenting today!
\( c = \frac{\Delta x}{\Delta t}
\)
Mathematical description
where:
- \( \Delta x \) is the path difference
- \( \Delta t \) is the time delay
Simulator
Dive into the fundamentals of light speed with our interactive speed of light simulator!
Interactive Physics Simulator – Image Formation by Concave Mirror
🌟 You May Also Like
Suggested experiments and activities based on your progress...
FAQs on Speed of Light
Qus 1. What is the speed of light in a vacuum?
The speed of light in a vacuum is approximately 299,792 kilometers per second (km/s) or 186,282 miles per second (mi/s). It is a fundamental constant of nature and denoted by the symbol “c”. This speed is the maximum limit at which all energy, matter, and information in the universe can travel.
Qus 2. Explain how the speed of light is measured in the above experiment.
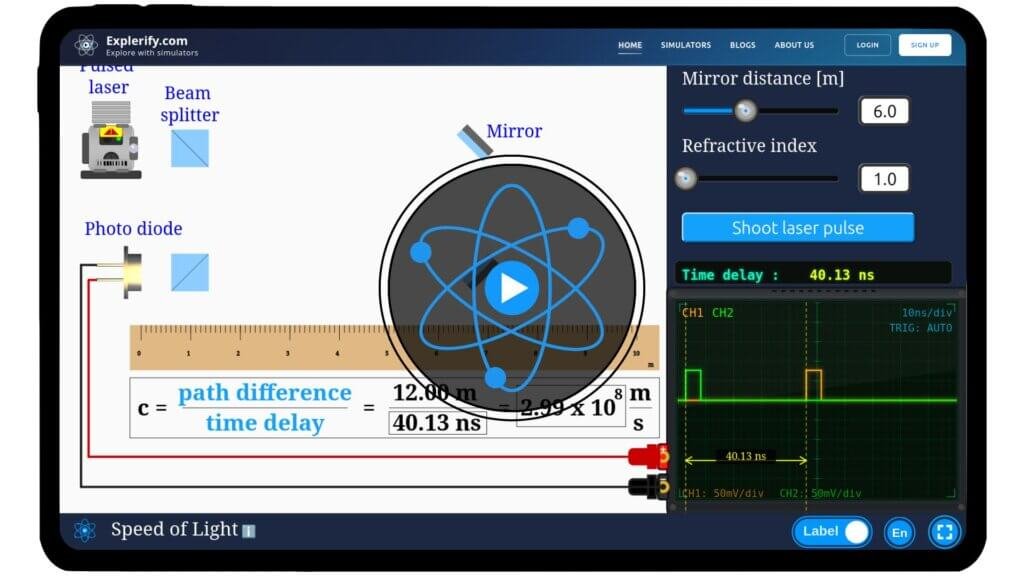
In this experiment, we measure the speed of light by making it travel an extra distance and recording the time it takes to do so.
A laser pulse is fired through a beam splitter, an optical device that divides the light into two parts—one part is reflected, and the other is transmitted.
The reflected beam travels directly to a second beam splitter, where it is reflected again and then detected by the sensor.
Meanwhile, the transmitted beam takes a longer path—it reflects off a pair of mirrors, passes through the second beam splitter, and then reaches the sensor.
By measuring the extra distance traveled by the transmitted beam and the time delay between the arrival of the two pulses at the sensor, we can calculate the speed of light.
Qus 3. Why is the speed of light important in physics?
The speed of light is crucial in physics because it underpins Einstein’s theory of relativity, connecting space and time. It serves as a universal constant in equations, such as \( E = m c^2 \) , defining the relationship between energy, mass, and the speed of light.
Qus 4. Does the speed of light change in different mediums?
Yes, the speed of light slows down when it travels through materials like water, glass, or air compared to a vacuum. This happens due to interactions with the particles in the medium, causing refraction. For example, light moves at about 225,000 km/s in water.
Qus 5. What are the most famous experiments that measured the speed of light?
The speed of light was first measured by Danish astronomer Ole Rømer in 1676 using the eclipses of Jupiter’s moons. Modern techniques, like the Michelson-Morley and Fizeau experiments, have refined its measurement using mirrors and lasers with extraordinary accuracy.
- Michelson conducted precise experiments in the late 19th century using rotating mirrors and long, measured distances. By reflecting light between mirrors and measuring the time delay, he calculated the speed of light as 299,796 km/s, earning him the Nobel Prize in Physics.
- Fizeau’s experiment in 1849 was the first terrestrial measurement of light speed. He used a rotating toothed wheel to interrupt a light beam and observed its reflection over a long distance.
Qus 6. What are modern techniques to measure the speed of light?
Modern techniques involve laser interferometry and highly accurate timing systems. Lasers are fired over known distances, and time-of-flight measurements are used to determine the speed. This method achieves extraordinary precision, confirming the speed of light as approximately 299,792 km/s.
Qus 7. Does the speed of light affect everyday technology?
Yes, technologies like GPS and communication systems rely on the speed of light. GPS satellites account for relativistic effects caused by the speed of light and time dilation to provide accurate positioning data.